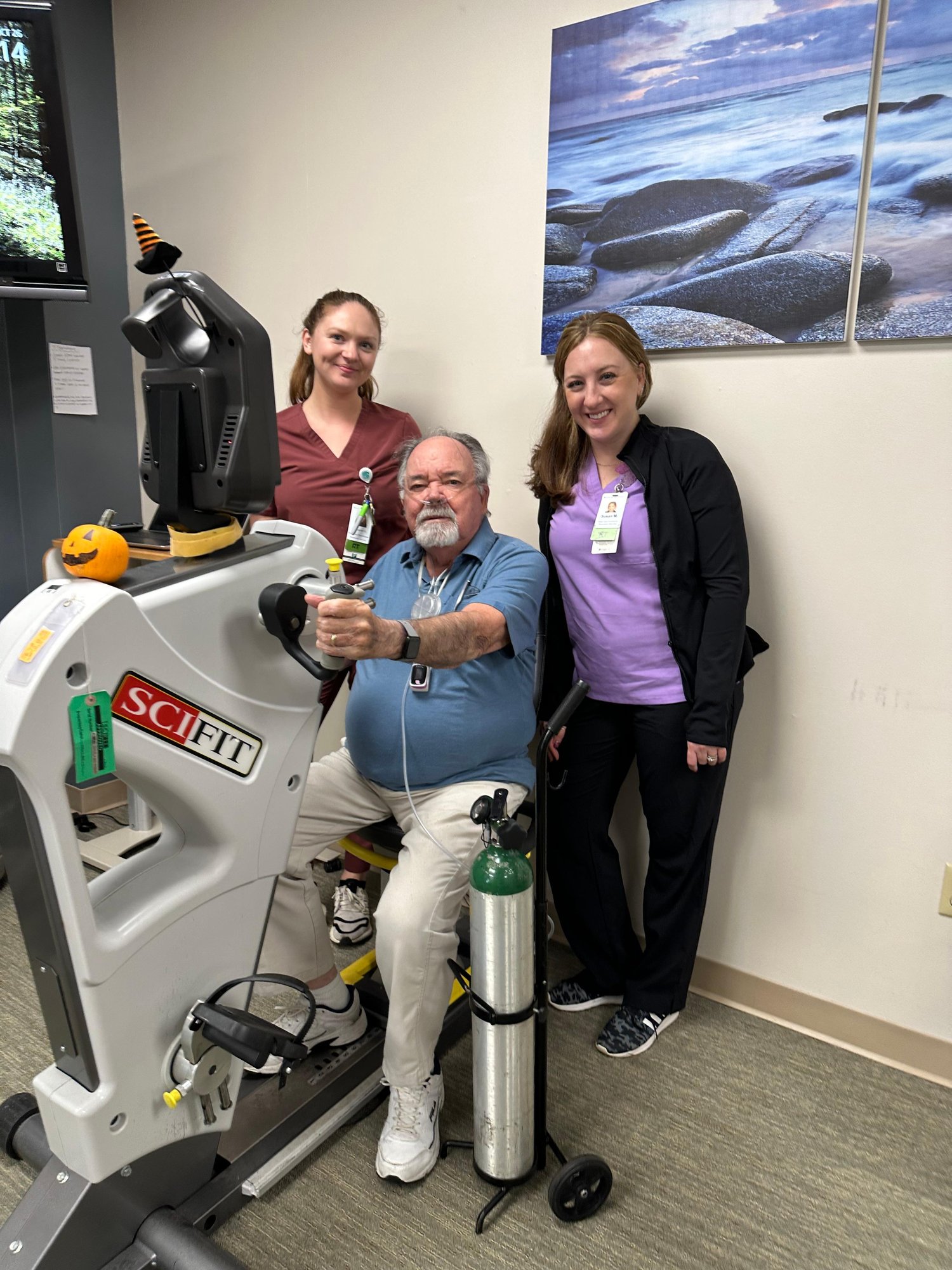
The Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation
Our Specialization is the difference
Housed within Gaylord’s Institute for Advanced Rehabilitation, the Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation leads cutting-edge research to improve outcomes for individuals with brain and spinal cord injuries, complex strokes, pulmonary diseases, and other complex medical conditions.
Get In Touch:
The Milne Institute
50 Gaylord Farm Road
Wallingford, CT 06492

Explore our current research initiatives driving innovation and advancing knowledge in healthcare.

Explore our latest published and presented works showcasing cutting-edge research and innovative discoveries.
Interested in partnering with us?
With our history of innovation, the researchers at Gaylord’s Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation - coupled with our nationally renowned physicians, therapists and clinicians - are the agile and insightful partners your brand can use to take your product to the next level.
David Rosenblum, MD | Medical Director, Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation
-5firstchoice.jpg?width=225&height=225&name=2020-11-20GAYLORDDR(DRDAVIDROSENBLUM)-5firstchoice.jpg) David Rosenblum, MD, is a board certified Physiatrist with subspecialties in SCI and Brain Injury Medicine. Along with conducting research and maintaining inpatient and outpatient clinical practices, Dr. Rosenblum serves as: The Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation Medical Director; UCONN PMR Residency Gaylord Site Director and Associate Program Director; Spaulding New England Regional SCI Model System Clinical Care co-Director and Gaylord Site Director; Yale School of Medicine Associate Professor of Neurology, and Orthopedics and Rehabilitation.
David Rosenblum, MD, is a board certified Physiatrist with subspecialties in SCI and Brain Injury Medicine. Along with conducting research and maintaining inpatient and outpatient clinical practices, Dr. Rosenblum serves as: The Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation Medical Director; UCONN PMR Residency Gaylord Site Director and Associate Program Director; Spaulding New England Regional SCI Model System Clinical Care co-Director and Gaylord Site Director; Yale School of Medicine Associate Professor of Neurology, and Orthopedics and Rehabilitation.
Pete Grevelding, MSPT, MBA; COO | Executive Director, Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation
 Pete Grevelding, MSPT, MBA is the Chief Operating Officer for Gaylord Specialty Healthcare and the Executive Director of the Milne Institution for Healthcare Innovation. He is responsible for the oversight of the clinical and operations areas. As Executive Director of the Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation, he has spearheaded the growth of Gaylord’s existing research and product development program. Pete is a Board-Certified Neurologic Clinical Specialist Emeritus.
Pete Grevelding, MSPT, MBA is the Chief Operating Officer for Gaylord Specialty Healthcare and the Executive Director of the Milne Institution for Healthcare Innovation. He is responsible for the oversight of the clinical and operations areas. As Executive Director of the Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation, he has spearheaded the growth of Gaylord’s existing research and product development program. Pete is a Board-Certified Neurologic Clinical Specialist Emeritus.
Henry “Hank” Hrdlicka, PhD | Director of Research, Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation
 Henry C. Hrdlicka, PhD, is the Director of Research at Gaylord Specialty Healthcare’s Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation. He works with the interdisciplinary clinical teams across Gaylord’s healthcare system and other leaders in healthcare and academia to develop innovative, pragmatic, and multidisciplinary studies. His goal is to design and implement novel evidence based rehabilitation practices that promote improved patient recovery, outcomes, and quality of life.
Henry C. Hrdlicka, PhD, is the Director of Research at Gaylord Specialty Healthcare’s Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation. He works with the interdisciplinary clinical teams across Gaylord’s healthcare system and other leaders in healthcare and academia to develop innovative, pragmatic, and multidisciplinary studies. His goal is to design and implement novel evidence based rehabilitation practices that promote improved patient recovery, outcomes, and quality of life.
Socheata Lim Morley, PhD | Research Coordinator, Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation
 Socheata L. Morley, Ph.D. is a Research Coordinator at Gaylord’s Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation. Dr. Morley is working on several clinical studies focused on advancing science and improving patients’ clinical outcomes. There, she oversees clinical trial design, data management and analysis, and manuscript preparation. Additionally, she oversees product development projects between Gaylord and external companies. Before joining Gaylord, Dr. Morley completed her Ph.D. in Biomedical Science at the University of Connecticut at UCONN Health.
Socheata L. Morley, Ph.D. is a Research Coordinator at Gaylord’s Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation. Dr. Morley is working on several clinical studies focused on advancing science and improving patients’ clinical outcomes. There, she oversees clinical trial design, data management and analysis, and manuscript preparation. Additionally, she oversees product development projects between Gaylord and external companies. Before joining Gaylord, Dr. Morley completed her Ph.D. in Biomedical Science at the University of Connecticut at UCONN Health.
John Corbett, BA | Research Coordinator, Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation
 John Corbett, Research Coordinator at Gaylord’s Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation, oversees clinical trials, oversees study design, study administration, data analysis, and manuscript preparation. Currently, Mr. Corbett is a part-time student at Oregon State University’s Data Analytics program, focusing on applied statistics. Prior to Gaylord, he graduated from Marist College (2020) with degrees in Psychology and Biology, and later working at the University of Vermont.
John Corbett, Research Coordinator at Gaylord’s Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation, oversees clinical trials, oversees study design, study administration, data analysis, and manuscript preparation. Currently, Mr. Corbett is a part-time student at Oregon State University’s Data Analytics program, focusing on applied statistics. Prior to Gaylord, he graduated from Marist College (2020) with degrees in Psychology and Biology, and later working at the University of Vermont.
Cynthia Bartholomew, MBA | Grant Specialist
 Cynthia Bartholomew is Gaylord's Grant Specialist. She shares 30+ years of experience in grant production and management, fund development, and nonprofit management. Her experience includes cultivating enduring donor relationships, expanding Boards of Directors, and diversifying funding sources. With an MBA from the University of Hartford and a BA in Psychology from SUNY Potsdam, she accomplishes program and budget development, grant submissions, and grant stewardship. Cynthia is an active member of the international Grant Professionals Association.
Cynthia Bartholomew is Gaylord's Grant Specialist. She shares 30+ years of experience in grant production and management, fund development, and nonprofit management. Her experience includes cultivating enduring donor relationships, expanding Boards of Directors, and diversifying funding sources. With an MBA from the University of Hartford and a BA in Psychology from SUNY Potsdam, she accomplishes program and budget development, grant submissions, and grant stewardship. Cynthia is an active member of the international Grant Professionals Association.
Roslyn Gilhuly, MA | Associate Vice President of Development
 Roslyn Gilhuly, Associate Vice President of Development, leads all fundraising initiatives at Gaylord. She brings more than three decades of experience in relationship building, donor cultivation and stewardship, strategic communications and nonprofit management to the team. Throughout her career, Roslyn has created campaigns to engage and expand donor relationships to maximize contributed revenue. Roslyn holds a Master’s degree from The American University (Washington, DC) and a Bachelor of Arts degree from Boston University (Boston, MA).
Roslyn Gilhuly, Associate Vice President of Development, leads all fundraising initiatives at Gaylord. She brings more than three decades of experience in relationship building, donor cultivation and stewardship, strategic communications and nonprofit management to the team. Throughout her career, Roslyn has created campaigns to engage and expand donor relationships to maximize contributed revenue. Roslyn holds a Master’s degree from The American University (Washington, DC) and a Bachelor of Arts degree from Boston University (Boston, MA).
Raquel Conklin, BSN | Nursing Professional Development Specialist
 Raquel Conklin, BSN, is a Nursing Professional Development Specialist in Gaylord Hospital’s Nursing Education Department. Ms. Conklin is responsible for coordinating new nursing staff orientations and the on-going educational needs of the Nursing Department. She also serves as a Nurse Residency facilitator and is the co-Chair of the Nursing Professional Practice Council. Prior to working in Nursing Education, she served as a Charge Nurse and Nurse Preceptor on one of Gaylord’s progressive care units.
Raquel Conklin, BSN, is a Nursing Professional Development Specialist in Gaylord Hospital’s Nursing Education Department. Ms. Conklin is responsible for coordinating new nursing staff orientations and the on-going educational needs of the Nursing Department. She also serves as a Nurse Residency facilitator and is the co-Chair of the Nursing Professional Practice Council. Prior to working in Nursing Education, she served as a Charge Nurse and Nurse Preceptor on one of Gaylord’s progressive care units.
Emily Meise, MS OTR/L, CLT, CBIS, CSRS | Level III Inpatient Occupational Therapist
E mily Meise, MS OTR/L, CLT, CBIS, CSRS, is a Level III Inpatient Occupational Therapist at Gaylord Specialty Healthcare since 2012. She earned her degrees at American International College. With 14 years of experience in various settings, she specializes in Stroke, Traumatic Brain Injury, and complex patient care. Meise researches cognitive screen development, the effects of robotics on upper extremity strength, balance perturbation in stroke patients, and visual field expansion after neurological injury.
mily Meise, MS OTR/L, CLT, CBIS, CSRS, is a Level III Inpatient Occupational Therapist at Gaylord Specialty Healthcare since 2012. She earned her degrees at American International College. With 14 years of experience in various settings, she specializes in Stroke, Traumatic Brain Injury, and complex patient care. Meise researches cognitive screen development, the effects of robotics on upper extremity strength, balance perturbation in stroke patients, and visual field expansion after neurological injury.
IRB Reviewed
All research projects are reviewed by our Institutional Review Board (IRB)
All research projects conducted at Gaylord are reviewed by our Institutional Review Board (IRB). This board includes professionals from disciplines throughout Gaylord and community leaders. Upon IRB approval, the studies are conducted within the guidelines of the submitted protocol. Annual reviews and audits are conducted to ensure projects are compliant. All research projects are required to earn and maintain IRB approval.
Gaylord's IRB is compliant with the U.S. Federal Government Department of Health and Human Service, Office for Human Research Protections. A Federal Wide Assurance (FWA00010599) that is valid through December 27, 2028, shows Gaylord’s commitment to comply with the requirements set forth in the regulations for the protection of human subjects. The Federal Wide Assurance defines the responsibilities of the Institution, the IRB, the IRB administrative office and staff, and the investigators to protect human research subjects.
For questions or inquiries, contact:
GaylordIRB@Gaylord.org
Through the Milne Institute for Healthcare Innovation, Gaylord Specialty Healthcare offers patients the opportunity to participate in various research projects. Inpatients and outpatients who are eligible to enroll in appropriate studies are given the information necessary to make an informed decision regarding participation. Gaylord staff works with other collaborating facilities to conduct and participate in larger studies, including some at an international level. There are also Gaylord-specific studies that are designed and conducted by Gaylord staff.
Conflict of Interest Statement
Conflicts of interest may occur when an investigator’s research responsibilities compete with his or her private interests, such as financial interests, raising concerns of objectivity and improper gain. Conflicts of interest are inevitable and may exist despite the highest standards of conduct and candor. Fortunately, most conflicts can be successfully resolved and managed without impeding research activities. Gaylord Hospital has adopted a policy requiring the disclosure of actual or potential conflicts of interest. A Gaylord Hospital Conflict of Interest Disclosure Form must be completed and submitted by investigators at the time of submission of research protocols to the IRB and at the time of a re-approval application. After disclosure, if any, the Gaylord Hospital Conflict of Interest Committee reviews the disclosure to determine how best to manage the conflict in a manner that protects both the research participants and the investigator. The policy applies to all investigators of faculty, staff, and students conducting sponsored research, all human subject research, animal subject research and research funded by a formal award from Gaylord Hospital based on submission of a proposal. A conflict of interest is defined as: “A situation associated with an investigator’s participation in Gaylord Hospital research where it reasonably appears, on an actual or potential basis that the investigator’s significant financial interest could directly and significantly affect the design, conduct or reporting of Gaylord Hospital research activities; or the investigator’s situation could directly and significantly compromise his or her professional commitments or allegiance to Gaylord Hospital.
Potential conflicts of interest and disclosures also apply to IRB members when they are assigned protocol applications for review. IRB members should consider possible or potential conflicts of interest and determine whether a particular role or relationship could affect his or her objectivity before reviewing, participating in a protocol discussion, or voting on a protocol application. Possible relationships to consider include: the IRB member is a listed investigator or advisor on an application; the member has a familial or close personal relationship with the investigator; the member holds a financial interest in the outcome of the research; or other concerns that warrant abstaining from review, deliberation and voting on a protocol. In the event of a potential conflict of interest, the IRB member should not accept the protocol for review and return the application for assignment to another member; or at full review meetings, any member(s) should disclose conflicts or simply state that participation is not appropriate and then recuse themselves from discussion and voting on the protocol.
